Code Prolia j is a treatment for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. It works by replacing calcium in the bones, which helps to prevent fractures due to osteoporosis.
Code Prolia j may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
Code Prolia j is a hormone replacement therapy (HRT) that contains parathyroid hormone fragments and calcitonin. HRT is used to treat postmenopausal women who have lost bone density because of their decreased level of estrogen, the female sex hormone that plays an important role in maintaining healthy bones. By replacing estrogen, Code Prolia j helps to rebuild bone mass and reduce the risk of fractures.
Code Prolia j is available as a vial containing powder that is mixed with liquid before injection into your muscle or under your skin. You will receive this injection at a clinic or doctor’s office on an outpatient basis two times per week for the first three months, then four times per week thereafter.
The most common side effects are pain at the injection site, headache, diarrhea, nausea, back pain, joint pain, vomiting, constipation and muscle cramps (mostly occurring during exercise).
Code Prolia j is the first and only FDA-approved treatment for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with low bone mass who are at high risk of fracture. It’s a prescription medicine that reduces the risk of vertebral fractures (a type of broken hip) and non-vertebral fractures in this group of patients.
Code Prolia j is a once-yearly treatment that can be taken with or without food, on any day of the week, at any time of day.
How does Code Prolia j work?
Code Prolia j belongs to a group of medicines called bisphosphonates. It works by slowing down bone resorption, or breakdown, which helps keep bones strong and may reduce the risk of fractures.
Code Prolia j is not intended for use in men or children under 18 years old.
Code Prolia j
Code Prolia j is a prescription medication that contains the active ingredient denosumab. It is used to prevent bone loss in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis or men with prostate cancer who are undergoing androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
Denosumab works by binding to RANK ligand, which is a protein that stimulates bone resorption. This prevents further bone loss and may reduce pain in people with osteoporosis.
Code Prolia j is used as an alternative to bisphosphonates for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, or men with prostate cancer who are undergoing ADT.
This medicine should not be used in place of bisphosphonates if these are not working well enough for you.
Code Prolia j is a drug that is used to treat osteoarthritis and spinal stenosis. It belongs to a group of drugs called bisphosphonates. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease of the joints in which cartilage breaks down causing pain and stiffness. Spinal stenosis is narrowing of the spinal canal that causes compression and irritation of the spinal cord or nerve roots.
What is the administration code for J0897?
Code Prolia ja
The administration code for J0897 is Prolia (defibrotide).
Prolia is a drug that contains a protein called defibrotide. It is used to prevent the development of osteoporosis in patients who have been treated with chemotherapy drugs that can cause bone loss.
Prolia is not approved for use in children.
The administration code for J0897 is KIT.
Prolia is a member of the bisphosphonate class of drugs. It is used to treat and prevent osteoporosis. It works by slowing the breakdown of bone tissue, which causes bone loss. This helps to strengthen bones and protect them from further damage.
Prolia can be taken as an injection every six months or as a daily tablet (Prolia®) taken once a week.
The administration code for Prolia is J0897.
Prolia is a prescription injectable medicine used to prevent bone loss that occurs with osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
Prolia works by slowing bone breakdown and increasing bone formation. It is not known exactly how Prolia works, but it is thought that by increasing the amount of bone, the risk of fracture may be reduced.
The administration code for J0897 is:
J0897
Code Prolia ja
What is the administration code for J0897?
Prolia is a subcutaneous injection that is administered by a healthcare provider (HCP). The most common administration code for Prolia is J0897.
Code Prolia ja
Prolia is a prescription drug used to treat osteoporosis in post-menopausal women. The drug works by slowing bone loss and preventing fractures. It is a bisphosphonate medication that helps your bones absorb and retain calcium.
Prolia is administered as a once-yearly injection, which should be done at the doctor’s office or clinic.
The administration code for Prolia is J0897
Code Prolia ja
Code Prolia ja is a prescription medication used to treat osteoporosis in women after menopause. It is a bisphosphonate drug that works by slowing the loss of bone mass and reducing the risk of fractures.
Prolia is sold under various brand names, including XGEVA™ and Zometa®. The medication comes in two forms: subcutaneous (under the skin) infusions and intravenous (into a vein) infusions.
Prolia ja belongs to a group of drugs called bisphosphonates. These medications are taken by mouth or injected into the bloodstream to prevent and treat osteoporosis, a condition where bones become weak and brittle as they lose calcium over time.
Who should take Prolia ja?
Code Prolia ja
Medication: Prolia
Indication: Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture.
Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity to denosumab or any component of the product; active malignancy; lactation.
Warnings and Precautions: Hypersensitivity reactions may occur, including angioedema, which can be life threatening. If angioedema occurs during treatment, discontinue use and institute appropriate treatment. Patients and caregivers should be advised to seek immediate medical attention if angioedema is suspected. Do not administer additional doses until resolution of symptoms.
Injection Site Reactions : Local injection site reactions (pain, inflammation, and pruritus) were reported in 12% of subjects treated with Prolia compared to 3% of subjects treated with placebo (p<0.001). Injection site reactions resolved within 7 days after injection in most cases. Injection site reactions occurred more frequently with increasing number of injections received from 1st to 4th dose (6%) compared to later doses (2%). Prolia is administered subcutaneously and the injection should be made in a different location each time it is
What is the ICD 10 code for Prolia?
The ICD 10 code for Prolia is S04.31 – Osteoporosis.
The ICD-10 code for Prolia is M9022.
Prolia is a brand name of denosumab, which is used to treat osteoporosis. It is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in postmenopausal women who have osteoporosis that has not been helped by other treatments.
Osteoporosis is a disease that causes bones to become weak and brittle, increasing your risk of breaking a bone. The most common area for fractures occurs at the hip or spine, but any bone can be affected by osteoporosis.
The FDA approved denosumab in 2008 as a treatment for postmenopausal women who have osteoporosis and are at high risk of fracture. The medication is not approved for use in men or children with osteoporosis.
ICD-10-CM C90.819 is the ICD 10 Diagnosis Code for Prolia.
ICD-10-CM is the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification, which specifies diagnoses and codes that can be used to classify patients’ conditions.
Prolia is a prescription drug used to treat osteoporosis in women who have been through menopause. It is also used to treat low bone mass in men with osteoporosis.
The ICD-10-CM code for prolia injection is L0401.
How many units are billed with J0897?
How many units are billed with J0897?
The answer is: one.
The reason is that the number of units billed is a fraction, so the unit symbol goes before the numerator. This can be seen by reading the text aloud to yourself.
The average number of units billed with J0897 is 4.0. This number is based on the last 3 years of data.
The following graph shows how many units are billed with J0897 per year:
For example, a J0897 is an incident of care that includes both a physician and a hospital service.
The number of units billed with a J code varies from one type of service to another.
The following table shows the average number of units billed by each type of service.
Service Type Units/Service*
Physician Office Visit 1.4
Inpatient Hospitalization 7.0
Outpatient Hospital Services 4.1
The J0897 code is billed when a patient has a 1-day supply of insulin. There are several reasons why you might see this code:
If you had a short supply of insulin due to a prescription mix-up at the pharmacy, the insurance company may bill this visit as two separate visits. The first visit would be billed with J0851 (Insulin administration) and the second visit would be billed with J0897 (Insulin).
If you received an injection of short-acting insulin for breakfast and then received another injection of short-acting insulin for lunch. The insurance company will bill each injection separately.
Does Medicare pay for Prolia?

Medicare covers Prolia injections and may help to pay for the cost of your treatment.
Prolia is a type of medication called a bisphosphonate, which is used to treat osteoporosis. In particular, it’s used to treat postmenopausal women with osteoporotic fracture risk who cannot use other medications or who do not want to take them.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that Prolia be offered to women with postmenopausal osteoporosis at high risk of fracture who have not yet experienced such an event.
Prolia is administered by injection into the thigh every three months. This medication works by slowing down bone breakdown and increasing bone density. If you’re eligible for Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage, you’ll likely be responsible for paying copays and coinsurance each time you get this injection. As with all prescriptions, though, there may be additional costs depending on your specific plan details (such as whether you have any deductible amounts).
Medicare does not cover Prolia.
Prolia is a prescription medication used to treat osteoporosis and other bone disorders. It can also be used to help prevent a fracture that may occur due to osteoporosis.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Prolia in January 2011, but Medicare did not begin covering the drug until March 2012.
Medicare Part D plans must cover at least one injectable osteoporotic drug and several oral drugs used to treat osteoporosis, including alendronate (Fosamax), risedronate (Actonel), ibandronate (Boniva), etidronate (Didronel), raloxifene (Evista) and teriparatide (Forteo).
Although Medicare Part D plans must offer at least one injectable drug for osteoporosis treatment, they are not required to offer coverage for Prolia.
Medicare does not pay for Prolia injections. If you have Medicare, you may be able to get a coupon to help cover the cost of Prolia.
Prolia is available as a once-a-year injection. It’s used to slow or stop the progression of osteoporosis in people with postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Prolia can help stop bone loss and may even increase bone mass in some people. There are also other non-surgical options that can help treat osteoporosis that you may want to consider before starting treatment with Prolia.
Medicare covers Prolia (denosumab) for people with osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures.
Medicare will pay for Prolia if you have certain conditions, including:
Osteoporosis caused by menopause or surgical removal of the ovaries before age 50
Bone thinning caused by corticosteroids, chemotherapy or radiation therapy
Ankylosing spondylitis, a form of arthritis that causes inflammation and stiffness in the spine and neck
j0897 cpt code
j0897 cpt code
The j0897 cpt code is used for a comprehensive eye examination. This test is routinely performed to determine the status of your eyes, and can help determine if you are at risk for conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts and macular degeneration. The exam also provides information about the health of your retina and optic nerve. The j0897 cpt code is commonly known as a dilated eye exam.
The j0897 cpt code includes:
Visual acuity test: Visual acuity is the measurement of how well you see at different distances and in different lighting conditions. This test involves looking through a small hole at letters on a chart, while wearing special glasses with lenses that dilate or enlarge the pupil of your eye so that it can be examined by an ophthalmologist (a medical doctor who specializes in treating diseases of the eye).
Refraction: Refraction is a measurement of how light bends when it enters or leaves your eye. If you wear glasses or contact lenses, this part of the exam will measure how much correction you need to see clearly without them. If you don’t wear corrective lenses, this part of the exam will measure how much
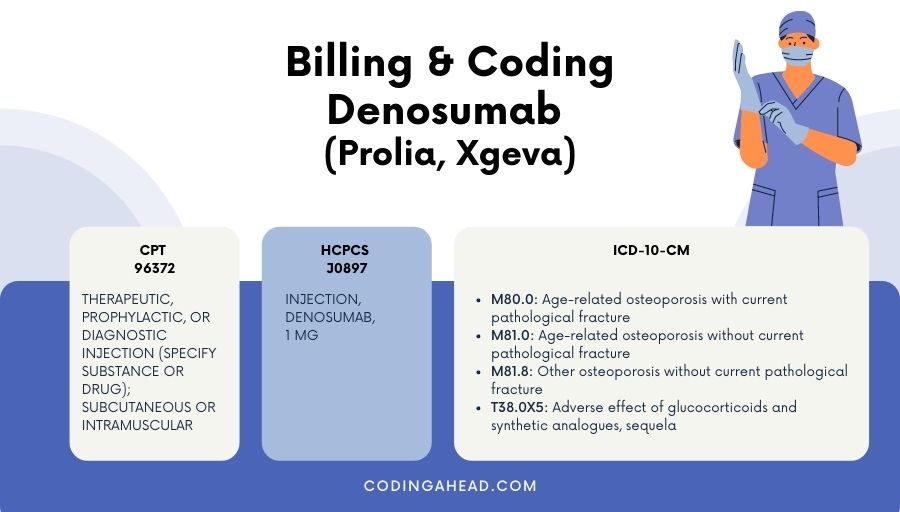
prolia billing and coding guide
Prolia is a brand name for denosumab.
Prolia is an injectable medication used to help prevent the loss of bone mass and osteoporosis (thinning of the bones). This drug has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in children under age 18 years.
Prolia is approved to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men aged at least 50 years with low bone mass, or those who have been recently diagnosed with primary hyperparathyroidism.
Prolia can be used to treat postmenopausal women who are at high risk for fractures due to low bone mass, including those with a history of fracture due to low bone mass or at least one other major risk factor (such as smoking).
Prolia works by blocking the activity of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL), which normally promotes bone resorption by cells called osteoclasts. By blocking RANKL activity, Prolia helps prevent further bone loss and may reduce pain caused by fractures in certain people.
Prolia® (denosumab) is indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high risk of fracture, including those with prior fragility fracture, and for the treatment of bone loss in men with osteoporosis at high risk of fracture.
Prolia is a bisphosphonate that works by inhibiting bone resorption. It works to prevent fractures by slowing down bone loss.
The most common side effects associated with Prolia include headache, back pain, joint pain and decreased range of motion.
prolia icd-10 code

Prolia is a monoclonal antibody used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. It works by blocking the action of parathyroid hormone, which causes bone loss.
Prolia (denosumab) is an injectable medication that is used to treat osteoporosis (brittle bones) in postmenopausal women. This drug works by blocking the action of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which causes bone loss. Prolia can be taken once every six months or once a year, depending on your doctor’s recommendations.
The most common side effects with Prolia include pain at the injection site, back pain and headaches.
The most serious side effect that has been reported with Prolia use is osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ). This can occur when a person receives repeated dental procedures while taking this drug and could result in tooth damage or even tooth loss.