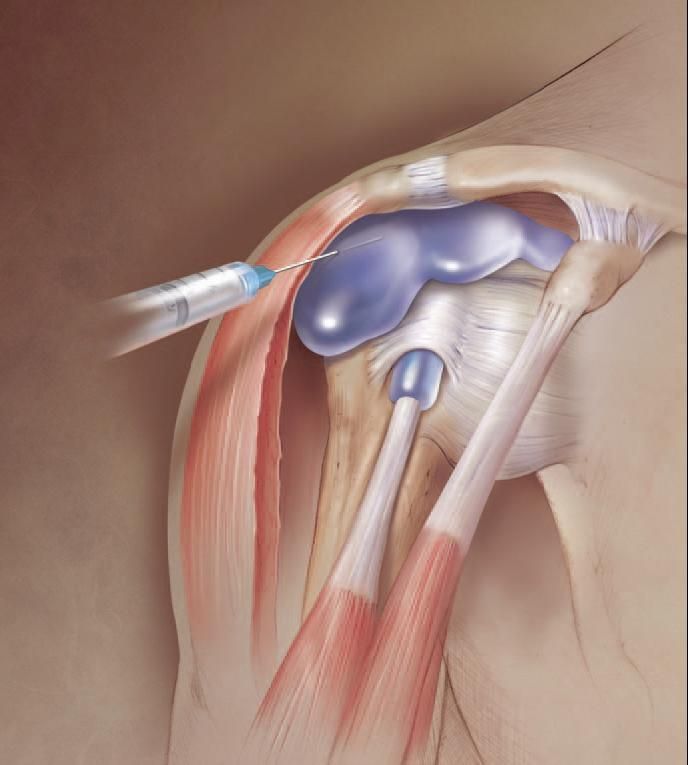
Cortisone Injection Shoulder Cortisone injections are the most common treatment for shoulder impingement syndrome. The cortisone injection is usually a single shot, but it may be repeated several times.
Cortisone is a steroid medication that reduces inflammation and swelling. It can reduce pain and improve your range of motion.
With this procedure, your doctor will inject a corticosteroid directly into the shoulder joint space to decrease inflammation and improve function. Cortisone injections can also be used to diagnose shoulder impingement syndrome and other shoulder problems by helping to determine if there’s a tear in your rotator cuff or labrum.
Cortisone injections offer relief from pain but don’t address the underlying cause of your symptoms. In some cases, they may delay surgery and allow you to try other conservative treatments first — such as physical therapy or NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
If you have persistent pain after an injection, it’s important to tell your doctor so you can receive further treatment options
How long does a cortisone shot last in the shoulder?
A cortisone shot is a type of injection that can be used to treat shoulder pain. The injection contains a corticosteroid, which is a medication that reduces inflammation and swelling.
Cortisone shots are sometimes called “steroid injections.” They are most commonly used for treating rotator cuff injuries or bursitis of the shoulder.
The exact length of time that the cortisone injection will last depends on several factors including:
Your age and general health
The cause of your shoulder pain (such as rotator cuff injury or bursitis)
How much steroid medication is injected into your shoulder
How long does it take for cortisone shot in shoulder to work?
The cortisone injection can help reduce pain and inflammation. It usually takes a couple of days for the cortisone shot to work, but it may take longer depending on the cause of your shoulder pain.
The doctor may need to do a test injection in one spot first to make sure your shoulder responds well to the steroid before giving you a whole series of injections to treat your pain. The doctor will also likely ask about your medical history, including any previous treatment for shoulder problems or other conditions like heart disease or diabetes. You should also tell him about any drugs you’re taking and if there are any allergies that would limit which shots he can give you.
You’ll probably be asked to lie face down on an exam table while the doctor injects your shoulder muscles with a local anesthetic first before giving you the steroid shot. He’ll then use a needle attached to a syringe (hypodermic needle) to give you a single injection into one of your shoulder muscles.
You’ll feel some pressure as he pushes the needle into your muscle, but it shouldn’t hurt too much — at least not as much as when you had your first symptoms of shoulder pain! You might feel some discomfort when he pushes on
Cortisone injection shoulder side effects
Cortisone injection shoulder side effects
Cortisone injections are usually given for pain relief. Cortisone is a naturally occurring hormone that your body makes in response to inflammation or injury.
Cortisone injections can be used to treat the following conditions:
Arthritis
Bursitis (swelling of the bursa)
Fractures and sprains
Exercise after cortisone injection in shoulder
The cortisone injection is an anti-inflammatory treatment that can be used to reduce pain, swelling, and stiffness in the shoulder. It is often used as a last resort when other treatments have not been effective in relieving shoulder pain caused by inflammation or injury.
There are many different conditions that may cause shoulder pain, including rotator cuff tendonitis, labral tears, bursitis and tendinopathy. These problems can be treated with cortisone injections, which may be helpful for several months.
Exercise after cortisone injection
To help prevent further damage to your rotator cuff muscles and tendons during recovery from a cortisone injection, you should avoid exercise until your doctor clears you to start working out again. Prior to returning to exercise, you should consult with your doctor or physical therapist about what types of exercises will best help strengthen your rotator cuff muscles and prevent future injuries.
Cortisone injection shoulder recovery time
If you are experiencing shoulder pain, you may be tempted to try a cortisone injection. However, this is not a permanent solution for your pain. Here’s what you should know about the recovery time after receiving a cortisone injection.
What is a Cortisone Injection?
Cortisone is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps reduce inflammation and swelling in the body. When injected into joints or soft tissues, it reduces swelling and pain associated with arthritis and other conditions.
When Should I See a Doctor About My Shoulder Pain?
If you’re experiencing chronic pain in your shoulder, it’s important to see your doctor for an examination and diagnosis as soon as possible. Your doctor will ask about your medical history, current symptoms, and any previous injuries or surgeries in order to make sure that you aren’t experiencing something serious like an infection or tumor growth in your joint capsule or rotator cuff tendons.
What happens if cortisone shot in shoulder doesn’t work
Cortisone injection is an effective treatment for many types of shoulder pain. It reduces inflammation and swelling, which can help relieve pain.
A cortisone shot in the shoulder typically lasts three to six months, but it may last longer depending on your condition. If the cortisone shot doesn’t work, your doctor may recommend other treatments.
If you have persistent shoulder pain after a cortisone shot, ask your doctor about other treatment options. These include:
Physical therapy
Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs)