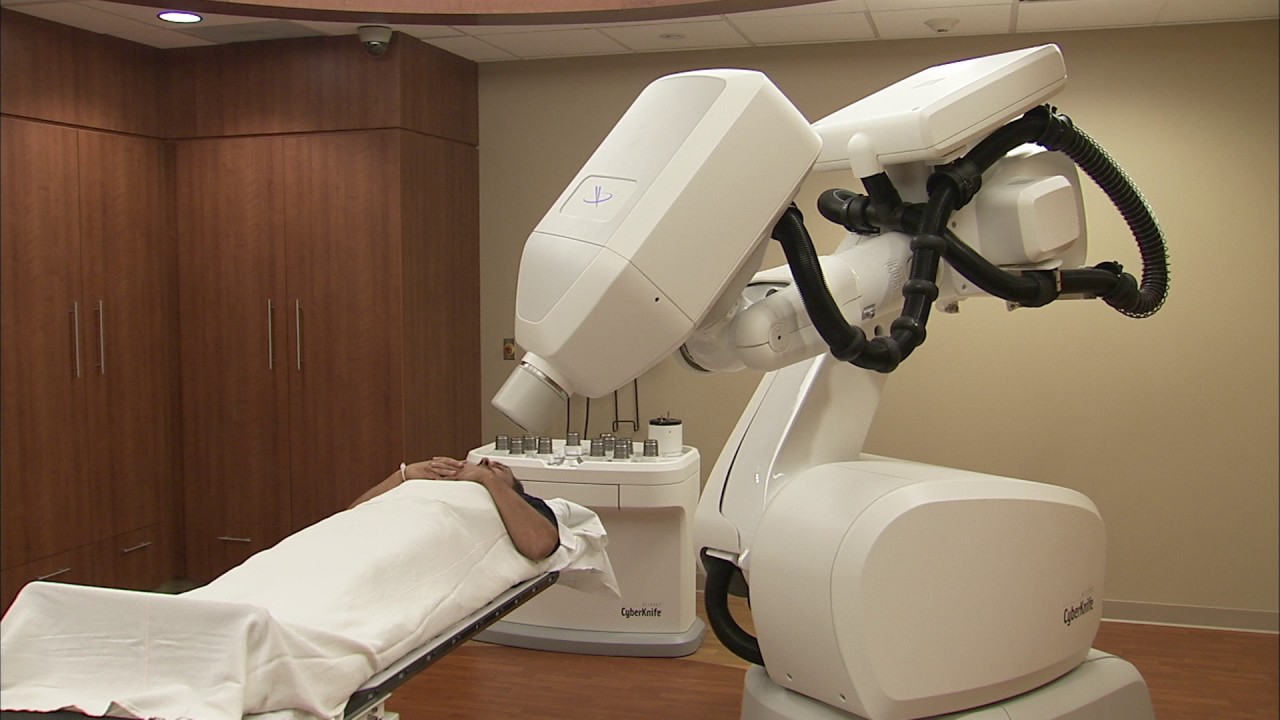
Cyberknife Breast Cancer Treatment; The Cyberknife® is a non-invasive treatment that uses radiotherapy to destroy cancerous tumors. The Cyberknife system uses an advanced robotic technology to deliver highly accurate, high doses of radiation at a speed that is up to 10 times faster than conventional MRIs. This allows us to treat patients in less time than traditional radiation treatments.
The Cyberknife system moves around your body according to the CT and MRI scans we take before your treatment. A computer-controlled machine will then move around your body and deliver radiation directly into the area where cancer cells are located.
CyberKnife’s precision and speed make it possible for us to target only the cancerous areas of the body, leaving healthy tissue unharmed.
Cyberknife breast cancer treatment is a non-invasive alternative to traditional radiation therapy. It’s a treatment option for people who have been diagnosed with breast cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes, or those who have metastatic breast cancer.
Cyberknife breast cancer treatment uses computer-controlled robotic technology to deliver targeted radiation directly to your tumor. This procedure is performed in an outpatient setting under general anesthesia, and it typically takes between 30 and 60 minutes.
During the Cyberknife Breast Cancer Treatment Procedure:
You will lie on an X-ray table while the machine moves around you, delivering precise doses of radiation as needed.
The Cyberknife Breast Cancer Treatment Procedure:
You will lie down during the procedure and be given anesthesia by anesthesiologists who specialize in this type of surgery. You will likely be awake during treatment but may feel some pressure or tingling sensation when the beam hits your breast. You may also feel slight discomfort if you move during treatment or if your position changes slightly from what was planned by the doctor beforehand. The entire procedure usually lasts about two hours, but most patients tolerate it well and are able to go home within a few hours after they wake up from anesthesia
What kind of cancer is CyberKnife used for?
CyberKnife is used to treat solid cancers, including lung cancer, brain tumors, and prostate cancer.
CyberKnife is most commonly used to treat lung cancer and brain tumors.
CyberKnife can be used to treat the following:
Brain tumors: CyberKnife can be used to treat benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous) brain tumors. It can also be used to treat metastatic brain tumors or recurrent brain tumors that have previously responded poorly to other treatments.
Lung cancer: CyberKnife is often used to treat lung cancer that has spread from somewhere else in the body (known as metastatic lung cancer). CyberKnife may also be used if you have lung cancer that has not responded well to other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
The CyberKnife system is used for the treatment of a variety of cancers and tumors, including:
Brain tumors including glioblastomas, metastatic brain tumors and brain metastases from other cancers
Spinal tumors
Thymoma (cancer of the thymus gland)
Breast cancer metastatic to the spine
Pancreatic cancer metastatic to the liver or spine
Cancers of the kidney or rectum, prostate, lung and other solid organs
CyberKnife is also an excellent choice for treating benign tumors.
CyberKnife uses radiation to destroy tumors in the brain, spine and other areas of the body.
CyberKnife is a robotic radiosurgery treatment that uses high doses of radiation to precisely target and treat tumors. Unlike traditional surgery, CyberKnife doesn’t require an incision or general anesthesia. This makes it a good option for people who have cancer on their spine, brain or throat.
CyberKnife is useful for:
Brain tumors: Primary brain tumors and metastatic brain tumors (tumors that have spread from elsewhere in the body) can be treated with CyberKnife radiation therapy.
Spinal cord tumors: Tumors located in the spinal cord can be treated with CyberKnife treatment if they’re causing symptoms such as weakness or numbness. The radiation is delivered through very thin needles inserted into the tumor. It destroys cancer cells while leaving healthy tissue intact.
Thyroid cancers: Thyroid cancers are usually treated with surgery followed by radioactive iodine therapy or surgery followed by chemotherapy. However, some people may not be able to undergo these procedures because they have other medical conditions or because their cancer has spread too far into surrounding tissues and lymph nodes. For these patients, CyberKnife
Can breast cancer be treated with CyberKnife?
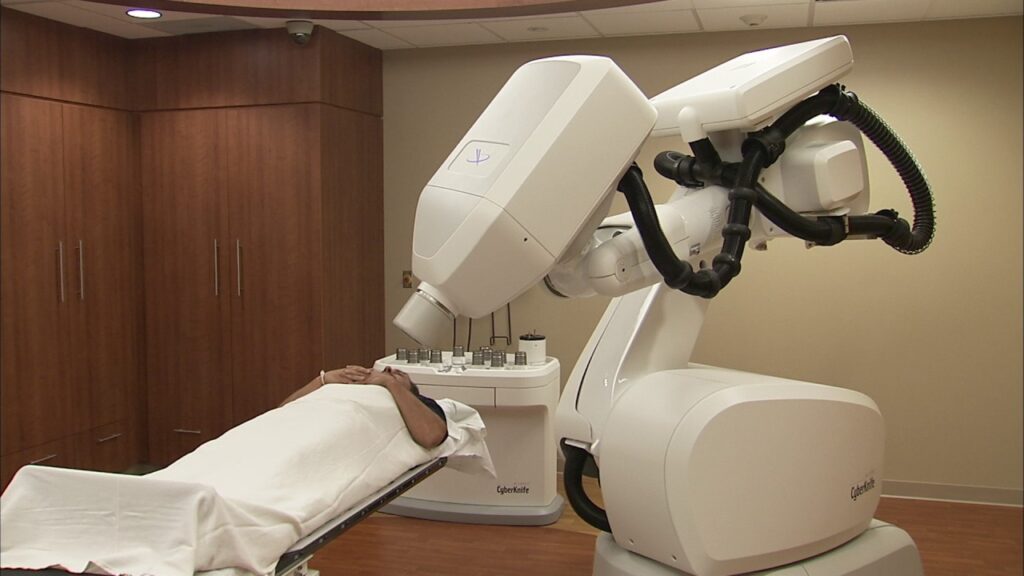
CyberKnife® is a non-invasive radiation therapy that uses advanced image-guided, stereotactic technology for precise, high dose delivery to tumors. CyberKnife is used to treat patients with a wide range of cancers and other diseases. The treatment is often used to relieve pain from spinal cord compression and metastatic bone disease, including painful bone metastases from breast cancer.
Breast cancer can be treated with CyberKnife when it has spread beyond the breast and into the bones of the spine or into the lungs. In these cases, chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy may not be effective in eliminating all cancer cells and controlling pain. CyberKnife treatment can provide relief from pain by destroying cancer cells in bone and lung tissue while sparing healthy tissue around them.
The CyberKnife is a robotic, noninvasive treatment that allows well-trained radiation oncologists to use the latest technology to treat cancer patients. It can be used to deliver high doses of radiation to tumors in hard-to-reach areas of the body with extreme precision.
The CyberKnife allows doctors to target tumors anywhere in the body, including those near vital organs or sensitive organs, like the brain and heart. The CyberKnife’s accuracy and precision allow for an unmatched treatment plan for each patient.
CyberKnife is most often used to treat cancers in the chest, abdomen, pelvis and spine, but it can also be used to treat cancers outside these areas if necessary
What is the difference between radiation and CyberKnife?
Radiation therapy is a treatment that uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy.
CyberKnife is a non-invasive radiation treatment that delivers targeted beams of radiation to precisely the location within the body where they are needed. The CyberKnife System allows for real-time imaging of the treatment area and enables physicians to make instantaneous adjustments in beam position and intensity during treatment.
Both radiation therapy and CyberKnife treatments are approved for use with most types of cancer, but there are some differences between them:
Radiation therapy uses beams of high-energy X-rays to destroy cancer cells in the body. CyberKnife uses a rapid sequence of precisely aimed X-ray beams that pass through healthy tissue without damaging it and converge on a tumor from different angles. The result is highly focused radiation delivered directly to the area of concern with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. The CyberKnife System allows physicians to make real-time adjustments in beam position and intensity during treatment, which can help minimize side effects while maximizing effectiveness
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be given in many ways, including:
Internal radiation therapy — also called brachytherapy — treats cancer that has spread to the inside of the body. Brachytherapy may be used for some types of cancer that have spread to the spine, brain or other organs. The doctor places small radioactive sources near the cancerous area. These sources emit radiation over time to destroy cancer cells.
External radiation therapy uses a machine outside your body to deliver radiation from outside your skin. External beam radiation therapy is commonly used to treat cancers of the breast, head and neck, prostate and lung among others. Internal radiation therapy requires an operation where radioactive material is placed directly into a tumor or nearby lymph nodes (also called brachytherapy).
CyberKnife is a type of radiotherapy that uses highly focused beams of radiation energy instead of x-rays to destroy tumors without damaging healthy tissue around them as much as traditional forms of radiotherapy do.
What is the best radiation treatment for breast cancer?
The best radiation treatment for breast cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s overall health.
Chemotherapy may be used to shrink the tumor before radiation therapy. This reduces the amount of radiation necessary to treat your cancer.
If you’re unable to tolerate chemotherapy, your doctor may recommend radiation therapy alone.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other types of electromagnetic energy to kill cancer cells in your breast. Radiation can also cause normal tissue around the tumor to die if it receives too much exposure to radiation, so doctors must carefully plan how much radiation will be given and where it will go.
Radiation therapy may be used to help destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. Radiation is usually given as external beam radiation or internal radiation therapy.
External beam radiation uses a machine outside the body to send radiation to the tumor and other parts of the breast. This type of treatment is often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells in the breast and prevent new ones from forming (recurrence).
Internal radiation therapy places radioactive material inside your body near the cancer cells. This type of treatment is used for early-stage or hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast. It may also be used for advanced-stage hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast if you can’t have chemotherapy due to side effects from previous treatments or other medical conditions that make it unsafe for you to have chemotherapy, such as heart disease or liver disease.
Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. Radiation can be used after surgery and chemotherapy to destroy any cancer cells that may remain. It can also be used before surgery to shrink tumor size, which can make it easier to remove the entire tumor with surgery.
Radiation therapy is usually given in a series of daily treatments over several weeks. The length of time and number of treatments needed depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the type and stage of breast cancer being treated.
Radiation therapy is sometimes used along with chemotherapy (chemo) or hormonal therapy (hormone). This combination treatment is called chemoradiotherapy (chemo-rad for short).
Breast cancer is a common cancer in women, with an estimated 207,030 new cases expected to be diagnosed in the United States in 2018. Treatment for breast cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing or spreading. It’s usually given after surgery to remove the tumor and before chemotherapy.
There are two main types of radiation therapy: external beam radiation and brachytherapy (internal radiation). Both types of treatment are effective at reducing the risk of recurrence (cancer coming back) after surgery.
External beam radiation therapy
External beam radiation therapy uses high-energy rays from a machine outside your body — you lie on a table while it moves around you. This type of radiation is sometimes called teletherapy.
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is another type of external beam radiation therapy that uses radioactive seeds in tiny metal capsules (brachy means “short”), which are inserted into your breast tissue near the tumor site during an operation and left there for several days or weeks until they no longer release any radioactivity. The seeds can also be implanted permanently under your skin during surgery if you get lymph node removal (sentinel lymph node
Who is a candidate for CyberKnife?

CyberKnife is a non-invasive, outpatient procedure that treats cancer anywhere in the body. It is used to treat tumors that cannot be removed surgically and those that are difficult to reach with other therapies.
Patients who might benefit from CyberKnife include those with:
Small, localized tumors (1 cm or less)
Multiple tumors affecting only one area of the body (such as lungs or liver)
Tumors that have spread throughout the body but have not yet metastasized (spread to other organs)
The following are examples of conditions that may be treated with CyberKnife:
Brain tumors, including glioblastoma multiforme and acoustic neuromas (tumors inside the skull)
Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
Lung cancer
CyberKnife is a non-invasive treatment to eliminate tumors and cancerous lesions. It is the only technology that can be used to treat tumors anywhere in the body, including deep seated tumors that cannot be removed surgically. The CyberKnife system uses sophisticated computer software and robotic technology to deliver precise radiation therapy with pinpoint accuracy. This sophisticated technology allows for an extremely high level of precision and accuracy in treating cancerous lesions.
CyberKnife is an excellent option for patients who have tumors or cancers located near critical structures such as the spinal cord, heart or brain. It may also be recommended for patients who have tumors or cancers that are difficult to reach with traditional radiation therapy methods or for those who are frail due to advanced age or other medical conditions (i.e., lung disease).
In addition, CyberKnife provides a treatment option for patients who have metastatic disease (the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body).
CyberKnife is an advanced form of radiotherapy, using a robotic system to deliver highly focused beams of radiation to tumors and other diseased areas. It uses image guidance to pinpoint the tumor and then creates a 3D map of the area, resulting in a more precise treatment plan than traditional forms of radiation.
CyberKnife is often used for cancer treatments, particularly lung cancer and head and neck cancers. It can also be used for pain management or to treat non-cancerous conditions such as spinal stenosis, trigeminal neuralgia or carpal tunnel syndrome.
CyberKnife is a noninvasive form of radiation treatment for cancer. In the CyberKnife system, patients are placed in a ring-shaped gantry that is surrounded by high-definition cameras and computer-controlled robotic arms. The robotic arms move around the patient as they are treated to target the tumor with a precise radiation dose.
The treatment is designed to deliver high doses of radiation directly to the tumor while sparing surrounding healthy tissue from exposure. This treatment can be used for patients who have been diagnosed with cancer in their brain, spine or prostate gland.
CyberKnife is also used for treating benign tumors such as acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma), meningioma and trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux).
What size tumor can CyberKnife treat?
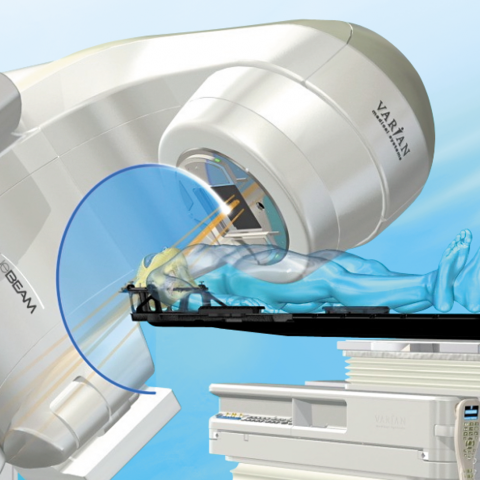
The CyberKnife System is capable of treating tumors of any size. The CyberKnife System is designed for use in conjunction with CT scans and MRIs, so it can be used to treat tumors anywhere in the body.
CyberKnife is a non-invasive, computer-guided radiation therapy that delivers highly accurate and conformal treatment to tumors. CyberKnife uses a delivery system that projects multiple high-powered beams of radiation from multiple angles to treat tumors in three dimensions. This enables the radiation beam to be shaped so that it conforms exactly to the shape of your tumor.
CyberKnife can treat tumors anywhere in the body, including the brain, spine, spinal cord, prostate gland, breast and lung (non-small cell). The following chart shows the approximate maximum size for each organ:
Lung: 6 cm
Prostate: 5 cm
Breast: 4 cm
Brain & Spine: 2 cm
The CyberKnife system is designed to treat tumors of any size or shape. The system can be used to treat tumors in most parts of the body, including the brain, spine and lungs.
The CyberKnife system has a wide variety of treatment options, including:
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) — This is the most common type of CyberKnife treatment. It is used to treat early-stage cancerous tumors that have not spread throughout the body (stage 1 or 2 disease). It also can be used to shrink large tumors or slow their growth so that other treatments may be more effective.
Pain management — CyberKnife therapy may be used for pain management after surgery if radiation treatments are not an option due to medical issues such as kidney failure or lung disease.
Brain metastasis — CyberKnife therapy may be used to reduce symptoms from brain metastasis (cancer spread from another part of the body). If a patient’s condition allows for it, surgery may also be an option for treating brain metastasis.
CyberKnife™ is a non-invasive, image-guided technology that offers real-time tumor tracking and precision targeting. The CyberKnife system consists of an integrated linear accelerator, a high-definition imaging system and proprietary software for controlling the treatment.
As opposed to traditional radiation therapy, which delivers beams of radiation through the body from multiple angles, CyberKnife uses a single beam of high-energy X-rays to treat tumors or other lesions in any part of the body. These beams are precisely targeted by computerized tracking systems that follow the movement of the tumor while it’s growing or shrinking during treatment.