Eczema Coxsackium; Eczema herpeticum, also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption, is a potentially fatal complication of atopic dermatitis (AD) and other pre-existing skin conditions with secondary superinfection by the herpes simplex virus.
Eczema coxsackium is a viral infection that causes a blister-like rash, usually on the hands and feet. It’s also called hand, foot and mouth disease. Symptoms usually last for 3 to 6 days. The main symptom of eczema coxsackium is a distinctive blistering rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The blisters can also appear on other areas of the body, including:
eczema herpeticum is a rare but serious complication of eczema. It occurs when the child’s skin is exposed to the herpes simplex virus (HSV). The infection, which is often caused by HSV type 1, can cause widespread blisters and sores on the body and face.
Fortunately, it can be treated with antiviral medications, if caught early.
Children with eczema are at an increased risk of eczema herpeticum because their skin barrier is weakened. This means that they are more likely to contract HSV than someone without eczema.
Another risk factor involves how your child’s eczema responds to steroid creams. If he or she has a history of “flaring” after discontinuing topical steroids, then he or she could be at an increased risk for developing eczema herpeticum and should see a dermatologist for further evaluation.
How does this happen?
eczema coxsackium develops when someone with atopic dermatitis comes in contact with the herpes simplex virus (HSV). HSV infections of the skin are common and include oral cold sores (usually caused by HSV type 1) and genital herpes (usually caused by HSV
There are seven types of hand, foot and mouth disease:
Aseptic meningitis. This is the most common type of coxsackievirus infection in adults, which can lead to a stiff neck and severe headaches.
Herpangina. Herpangina causes fever, mouth sores and sometimes vomiting. Herpangina usually affects children younger than age 5.
Pericarditis. This condition involves inflammation of the tissue surrounding the heart (pericardium). Symptoms include chest pain, fever and trouble breathing. The pain is often worse when lying down, coughing or swallowing.
Pleurodynia (“Bornholm disease”). Bornholm disease is marked by sudden onset of chest pain, which worsens when taking a deep breath or coughing. Other symptoms include fever and muscle aches in the upper back and abdomen (stomach area).
Eczema coxsackium. A viral skin infection that can cause blisters on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet or buttocks in infants or children with atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease. This illness is most common in children younger than age 10 and causes sores in the mouth and a rash on
What is eczema?
Eczema is the name for a group of conditions that cause skin to become red, itchy, inflamed, and sometimes blistering and weeping. Dermatitis and eczema are not the same thing. A person can have dermatitis or eczema or both. “Dermatitis” means inflammation of the skin.
There are different types of eczema: atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, nummular eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and stasis dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is very common in infants and children but can occur at any age.
What causes eczema?
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown. In people with atopic dermatitis the skin barrier is disrupted. This allows moisture out and germs in more easily and makes the skin more sensitive to irritants. The immune system overreacts to these germs, causing inflammation and itching.
What are the symptoms of eczema?
Symptoms include reddened skin that may be very itchy, especially in infants; rashes on the face, inside the elbows and behind the knees; small bumps (pap
Coxsackie virus is the cause of the disease of Coxsackie. This virus belongs to a group called enteroviruses, which also includes polio and hepatitis A.
Coxsackie infection usually causes a mild fever, sore throat, fatigue and headache followed by blisters on your hands and feet. In children, coxsackie can also cause herpangina (blisters in the back of your mouth) and rashes such as hand-foot-and-mouth disease.
eczema herpeticum
Erythema multiforme minor
Exfoliative dermatitis
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
What is Eczema Coxsackium?
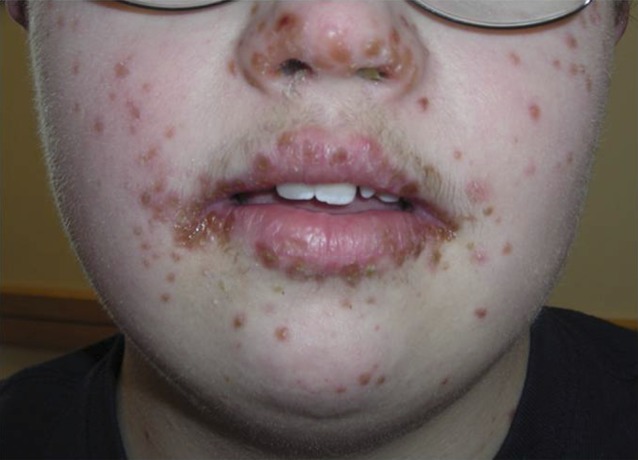
Eczema coxsackium is a rare form of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). It typically occurs in children.
It’s characterized by a rash on the hands and feet. The rash forms blisters that are similar to those that appear in patients with hand, foot, and mouth disease.
It’s caused by the coxsackievirus A16 virus.
What is eczema Coxsackium?
Eczema Coxsackium is a type of hand, foot and mouth disease. It’s caused by a virus called coxsackievirus A16. This is one of the viruses that can cause hand, foot, and mouth disease.
This viral infection usually starts with:
fever
loss of appetite
blisters on the feet or hands
The blisters may also appear in the mouth, anus, or genital area. They’re often small, painful, and filled with fluid. You can have as few as three or as many as 500 blisters at a time.
Eczema coxsackium is a blistering form of eczema that’s usually caused by Coxsackie A16, a virus from the Coxsackie family.
It’s common in children between the ages of 5 months and 3 years. It typically appears on the hands and feet, but can also develop in other areas including the buttocks and face.
Eczema coxsackium is not contagious once the blisters have been present for at least 48 hours.
If your child develops eczema coxsackium, it doesn’t mean they have a weak immune system or that they’re more likely to develop other skin conditions.
Eczema coxsackium is a viral infection that causes eczema (atopic dermatitis). It most commonly affects infants and young children who have atopic dermatitis.
Eczema coxsackium can cause painful blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It usually resolves after a few weeks
Eczema coxsackium is a viral infection of the skin caused by the coxsackievirus. It was first identified in 1943 and is also known as hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) or vesicular stomatitis.
Eczema coxsackium occurs most frequently in infants and children under 10 years old, though it can occur in adults. It is relatively common. According to a study published in the journal Pediatric Dermatology, HFMD affects 2–13 percent of people across the globe.
The most common symptoms of eczema coxsackium are:
small, red bumps and blisters on the palms of hands, soles of feet and inside of mouth
the rash usually appears on both hands and feet and spreads to the mouth
skin lesions may also appear on the buttocks or genitals
Coxsackie is a virus in the same family as poliovirus. This virus causes a skin rash called eczema herpeticum that occurs in those who have atopic dermatitis or eczema.
Coxsackie is very contagious and spreads easily from one person to another through direct contact with broken skin or secretions from the nose and throat of an infected person. Coxsackie can also spread through contaminated objects such as towels, clothing, and toys.
Most people with coxsackievirus infection have no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they often appear as a cold (runny nose, cough) followed by a blister-like rash. The rash begins to appear several days after the cold symptoms begin. It usually starts on the neck and face, then spreads to the rest of the body. It can be itchy and painful but usually goes away within 2 to 3 weeks.
Eczema herpeticum is a serious condition caused by Coxsackie virus. The virus infects the broken skin of eczema patients and causes numerous fluid-filled blisters (vesicles). It usually appears on the head, but may spread to other parts of the body including palms, soles, buttocks
Eczema herpeticum, also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption, is a herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. HSV-1 and HSV-2 can both cause eczema herpeticum. Signs and symptoms include blisters and sores that ooze fluid.
Risk factors for eczema herpeticum include people with a weakened immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS or who have undergone an organ transplant. Eczema herpeticum is treated with antiviral medication and antibiotics.
What Causes Eczema Coxsackium?

What is eczema Coxsackium?
Eczema coxsackium is a rare form of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). It typically occurs in children.
It’s characterized by a rash on the hands and feet. The rash forms blisters that are similar to those that appear in patients with hand, foot, and mouth disease.
It’s caused by the coxsackievirus A16 virus.
What is eczema Coxsackium?
Eczema Coxsackium is a type of hand, foot and mouth disease. It’s caused by a virus called coxsackievirus A16. This is one of the viruses that can cause hand, foot, and mouth disease.
This viral infection usually starts with:
fever
loss of appetite
blisters on the feet or hands
The blisters may also appear in the mouth, anus, or genital area. They’re often small, painful, and filled with fluid. You can have as few as three or as many as 500 blisters at a time.
Eczema coxsackium is a blistering form of eczema that’s usually caused by Coxsackie A16, a virus from the Coxsackie family.
It’s common in children between the ages of 5 months and 3 years. It typically appears on the hands and feet, but can also develop in other areas including the buttocks and face.
Eczema coxsackium is not contagious once the blisters have been present for at least 48 hours.
If your child develops eczema coxsackium, it doesn’t mean they have a weak immune system or that they’re more likely to develop other skin conditions.
Eczema coxsackium is a viral infection that causes eczema (atopic dermatitis). It most commonly affects infants and young children who have atopic dermatitis.
Eczema coxsackium can cause painful blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It usually resolves after a few weeks
Eczema coxsackium is a viral infection of the skin caused by the coxsackievirus. It was first identified in 1943 and is also known as hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) or vesicular stomatitis.
Eczema coxsackium occurs most frequently in infants and children under 10 years old, though it can occur in adults. It is relatively common. According to a study published in the journal Pediatric Dermatology, HFMD affects 2–13 percent of people across the globe.
The most common symptoms of eczema coxsackium are:
small, red bumps and blisters on the palms of hands, soles of feet and inside of mouth
the rash usually appears on both hands and feet and spreads to the mouth
skin lesions may also appear on the buttocks or genitals
Coxsackie is a virus in the same family as poliovirus. This virus causes a skin rash called eczema herpeticum that occurs in those who have atopic dermatitis or eczema.
Coxsackie is very contagious and spreads easily from one person to another through direct contact with broken skin or secretions from the nose and throat of an infected person. Coxsackie can also spread through contaminated objects such as towels, clothing, and toys.
Most people with coxsackievirus infection have no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they often appear as a cold (runny nose, cough) followed by a blister-like rash. The rash begins to appear several days after the cold symptoms begin. It usually starts on the neck and face, then spreads to the rest of the body. It can be itchy and painful but usually goes away within 2 to 3 weeks.
Eczema herpeticum is a serious condition caused by Coxsackie virus. The virus infects the broken skin of eczema patients and causes numerous fluid-filled blisters (vesicles). It usually appears on the head, but may spread to other parts of the body including palms, soles, buttocks
Eczema herpeticum, also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption, is a herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. HSV-1 and HSV-2 can both cause eczema herpeticum. Signs and symptoms include blisters and sores that ooze fluid.
Risk factors for eczema herpeticum include people with a weakened immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS or who have undergone an organ transplant. Eczema herpeticum is treated with antiviral medication and antibiotics.
