How do guys get epididymitis?
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, which is a tube that connects to the sperm-producing testicle. The epididymis stores and carries sperm after they leave the testicles. There are several possible causes of this infection, including sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
A doctor will often treat epididymitis with antibiotics, but other treatments may also be used depending on the cause. If you have symptoms of epididymitis or think you may have it, see your doctor as soon as possible.
What causes epididymitis?
There are many different causes of epididymitis:
Epididymitis is a common condition that causes pain and swelling of the epididymis, the structure where sperm is stored in men.
The most common cause of epididymitis is infection. Bacteria, viruses or fungi can all infect the epididymis. Other causes include:
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhoea and chlamydia infections
Use of anabolic steroids – these are drugs taken to build muscle mass and strength, which can have harmful side effects on the body
Infections of the prostate gland – a gland found below the bladder that surrounds part of the urethra (tube that carries urine from your bladder)
Trauma to the scrotum – such as being hit by a baseball pitch or kicked in the groin area
Most cases of epididymitis are caused by bacterial infections. A number of different bacteria can cause epididymitis, including enteric organisms (like E coli) and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
In men who have sex with men, the most common cause of epididymitis is gonorrhea, a bacterial infection that can be transmitted through oral, vaginal and anal sex. Other STDs that can lead to epididymitis include:
Chlamydia
Genital herpes
HIV/AIDS
Syphilis
According to the Mayo Clinic, epididymitis is a painful condition that affects the epididymis, a tube that connects the testicle to the vas deferens. The inflammation of this structure can cause discomfort and pain in one or both testicles.
Symptoms of epididymitis include:
Pain and swelling of one or both sides of the scrotum
Fever, chills and general malaise (a feeling of being unwell)
Testicle pain that increases when you cough, sneeze or lift something heavy
How did my boyfriend get epididymitis?
How did my boyfriend get epididymitis?
Epididymitis is an inflammation of a tube called the epididymis that’s attached to the back of a man’s testicles. The epididymis stores sperm that have matured and are ready for ejaculation.
An infection can cause epididymitis, which can be caused by bacteria or a virus. It can also happen when you have a kidney stone in your bladder or prostate gland. Epididymitis is not cancer and doesn’t cause infertility (the inability to father children).
How did my boyfriend get epididymitis?
My boyfriend is suffering from epididymitis. He had sex a few days ago and it was unprotected, but he tested negative for HIV, gonorrhea, chlamydia and syphilis. How did he get this infection?
Epididymis is an organ in the male reproductive system where sperm matures. There are two epididymides (one on each side). The epididymis is connected to the testicle by a tube called vas deferens. Sperm moves from the testicles through the vas deferens into the epididymis where it matures for about 3 weeks before it leaves the body during ejaculation. When there is infection in epididymitis, it may cause swelling and tenderness on one of both sides of the testicle or on the vas deferens which passes through the testicle up to its junction with other structures like seminal vesicle gland (a gland that produces seminal fluid), prostate gland (gland that produces fluid that lubricates semen), Cowper’s glands (glands that produce pre-ejaculate) and urethra (tube that carries urine out of
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, a tube that carries sperm from the testicles to where it mixes with fluids from other parts of the male reproductive system to become semen.
It’s not uncommon for men to get epididymitis, and it can happen at any age. In most cases, it’s not serious and will go away on its own within a few days or weeks.
The cause of epididymitis is usually an infection caused by bacteria or a virus. Sometimes it may be caused by an injury to your genitals or urinary tract.
How did my boyfriend get epididymitis?
The most common cause of epididymitis is an infection from sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). These infections include gonorrhea, chlamydia and syphilis, which can all spread through unprotected vaginal sex or anal sex. Men are more likely to develop these bacteria-related infections because they have longer urethras than women do — making them more susceptible to bacteria entering their bodies through the urethra during sex.
Because the symptoms of epididymitis are similar to those of many other conditions (such as prostatitis), it’s important that you see your doctor if you think you might have this condition
A man’s testicles are located inside his scrotum, which is the loose sac of skin that hangs behind the penis. The epididymis is a long, coiled tube that connects the testicle to the vas deferens (the tube through which sperm travel). The epididymis stores and matures sperm before they move on to the vas deferens.
Sperm can become unhealthy in two ways:
Sperm DNA damage: The sperm can be damaged by free radicals or other toxins in your body. This most often happens when you’re exposed to high levels of radiation or toxins like pesticides or herbicides.
Sperm motility problems: Motility is how well the sperm swims, and it’s affected by many factors, including temperature and nutrition. Men who have diabetes or heart disease may have trouble making enough healthy sperm. A lack of zinc (a mineral) also affects both motility and DNA damage in sperm cells.
Can you get epididymitis without STD?

Yes. You can get epididymitis without having an STD.
In fact, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the most common cause of epididymitis is a urinary tract infection (UTI). In fact, the NIH says that about 25 percent of people who have UTIs develop epididymitis.
Epididymitis can also result from other causes such as:
Swelling and irritation of the epididymis caused by trauma or injury to the scrotum, like being kicked in the testicles or falling on a hard object
Inflammation of an epididymal cyst (a fluid-filled sac)
Trauma or injury to your testicles
A sexually transmitted disease that can spread to the epididymis
Epididymitis is a type of pelvic inflammatory disease that affects the epididymis, a tube that connects the testicle to the vas deferens (the tube that carries sperm). It can result from infection with bacteria or a virus, but it’s also possible to get epididymitis without an STD.
Epididymitis Causes
Although the majority of cases of epididymitis are caused by STDs, there are other potential causes:
Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia)
Mycoplasma genitalium (MG)
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, a small tubular structure behind and above each testicle that stores and carries sperm.
Epididymitis usually occurs in men who have a sexually transmitted disease (STD). But the condition can also occur without an STD.
In most cases, the cause of epididymitis is unknown. But it may be caused by:
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia and HIV/AIDS
Urinary tract infections, kidney stones and other conditions that affect your urinary tract
Injury to your testicles or upper thigh area
Testicular torsion (a twisting of your testicle that cuts off its blood supply)
Epididymitis is a painful inflammation of the epididymis, a coiled tube at the back of the testicle that connects to the vas deferens. The condition can range from mild to very serious, but it’s usually manageable with rest and medication.
Causes
Epididymitis is often caused by an infection, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. But not everyone who gets an STD will develop this condition. It can also be caused by bacteria entering the body through small cuts or tears in the skin around the testicles. In rare cases, it’s due to an allergic reaction to certain medications or other substances.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms include:
Painful swelling in one or both testicles
Pain in your lower abdomen, groin or scrotum (the sac that holds your testicles)
Fever and/or chills
Nausea and vomiting (if your infection becomes severe)
Can a woman give a man epididymitis?
Yes, a woman can give a man epididymitis.
The epididymis is a coiled tube in the male reproductive system that stores sperm after it leaves the testes. Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis that can result from sexually transmitted infections (STIs), urinary tract infections, kidney stones or other causes. The condition is most commonly associated with gonorrhea and chlamydia, but it can occur after other types of infection as well.
Signs and symptoms of epididymitis include:
Painful swelling of the testicles
Painful urination
Fever
Yes, a woman can give a man epididymitis.
The epididymis is the tube that connects to the testicle and stores sperm before they are ejaculated. Epididymitis is inflammation of this tube. The inflammation can be caused by infection, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, or by an injury to the area. The most common type of injury is from vigorous sexual activity (such as rough sex).
The symptoms of epididymitis include pain in the scrotum along with pain when urinating and/or ejaculating. The swelling will usually go away after a few days, but if it doesn’t then you should see your doctor for treatment.
Yes, a woman can give a man epididymitis.
The epididymis is a tightly coiled tube that connects the testicles to the vas deferens and carries sperm from the testicles to the ejaculatory ducts. It’s also one of the most common sites for bacterial infections in men.
The infection can be caused by sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, or by non-sexually transmitted bacteria, such as E. coli. The condition can also result from trauma to the scrotum or back passage during sex.
Women are not immune to epididymitis either — it’s just less common in women than in men because they don’t have epididymides.
The answer is yes.
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, a tube that connects the testicles to the vas deferens. The epididymis stores and transports sperm.
The infection can be caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites. Most cases of epididymitis are due to one of these infections but it can also be caused by injury or surgery (especially vasectomy).
A woman can transmit the virus that causes epididymitis directly through sexual intercourse or indirectly through other body fluids such as blood, saliva, urine and feces. In addition, a woman may pass on certain bacteria that cause epididymitis if she has an infection in her vagina or urethra.
Can you give epididymitis to your partner?

Can you give epididymitis to your partner?
No, epididymitis is not contagious. It is not possible to pass on this condition from one person to another.
However, it is possible for the bacteria that cause epididymitis to be passed on from one person to another through sexual contact.
If you have had an infection of the epididymis and you wish to conceive a baby, you should wait until at least three months after recovery before trying for a baby.
The answer is yes, you can give epididymitis to your partner.
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, which is a tube that carries sperm from the testicles. It’s usually caused by a bacterial infection and may be accompanied by a fever, pain or swelling in the scrotum.
If you have epididymitis, it can last from a few days to several weeks and occasionally longer. While it goes away on its own without treatment, there are some things you can do to speed up the process:
Rest — Take it easy while you have epididymitis so that your body can focus on healing itself instead of fighting off an infection.
Drink plenty of fluids — Drinking lots of water will help flush out bacteria from your urinary tract and make sure that you don’t become dehydrated while you’re sick.
Take acetaminophen — This common over-the-counter drug works well for reducing fever and relieving pain associated with epididymitis. Acetaminophen is available as Tylenol and many other brand names; check with your doctor before taking any medication while pregnant or breastfeeding because Tylenol has been linked to fetal abnormalities when used during pregnancy or
Yes, you can give epididymitis to your partner.
The epididymis is a tube that stores sperm before it leaves the testicle, and it can become inflamed if you contract an STD or get an infection. This condition is called epididymitis, and it’s usually caused by a bacterial infection.
If you have this condition, your testicles may swell and feel tender. You might also experience pain while peeing, but the symptoms aren’t always severe enough to require medical treatment.
In rare cases, epididymitis can lead to infertility if left untreated.
You can get epididymitis through sexual contact with someone who has it. However, this isn’t likely unless they’re experiencing symptoms when you have sex with them — which means that you’d have to have sex with them at a time when they’re not feeling any pain in their testicles or scrotum.
Yes. The epididymitis is a bacterial infection of the epididymis and is contagious. Epididymitis usually occurs as a result of an infection of the urinary tract. Bacteria can enter the body through the urethra (the tube that carries urine from your bladder to outside your body) or from anal sex.
The most common symptom is pain in the scrotum that gets worse when you have an erection. It may be accompanied by fever, nausea and vomiting, but these symptoms are less common than pain.
You can get it from having unprotected sex with someone who has it, so it’s important to use condoms every time you have sex with someone new or if you share any sexual equipment (dildos, vibrators etc). In addition, make sure you wash your hands after touching your penis or testicles before touching anything else (such as your partner).
Does ejaculating hurt epididymitis?
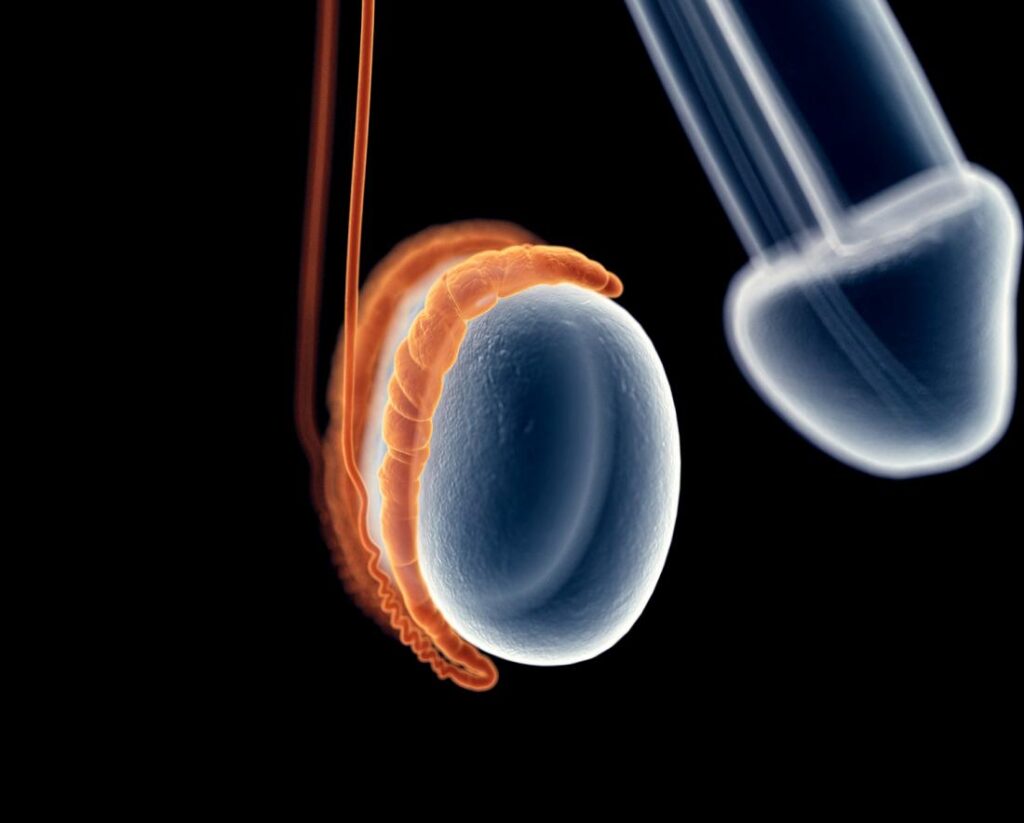
There is no evidence that ejaculation causes epididymitis.
Ejaculation may be associated with pain or swelling in the testicles. This is usually associated with a urologic infection such as epididymitis or orchitis. The symptoms can include pain in the testicle, scrotum, or groin area; swelling of one or both testicles; and fever. Symptoms usually occur within hours after ejaculation, but they can occur as long as seven days later.
Ejaculation does not always cause pain. If it does, it may be a sign of something more serious, like epididymitis.
Ejaculation is the release of semen from the penis. There are two types of ejaculation:
Ejaculation
Ejaculation is the release of semen from the penis. There are two types of ejaculation:
Psychogenic ejaculation: This occurs when sexual arousal causes orgasm without any physical stimulation of the genitals or pelvic area.
Reflexive ejaculation: This occurs during sexual stimulation or in response to an erotic stimulus, such as a picture or video.
Ejaculation is the release of semen from the penis. It is an important part of sexual activity in humans and other animals. In male humans, ejaculation is usually accompanied with orgasm.
Ejaculation is a reflex comprising a series of muscle contractions that start in the vas deferens, move through the prostate and urethra, and end in a coordinated contraction of pelvic muscles that expels semen from the urethra. The process takes from three to ten seconds if not interrupted by premature ejaculation (PE).
Ejaculations per week: average 8-10
Can epididymitis spread through oral?
Yes, epididymitis can spread through oral sex.
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis, a structure at the back of the testicle that stores sperm. It’s caused by an infection and is generally treated with antibiotics.
While it’s not well-known, epididymitis can also be transmitted through oral sex. The condition is usually caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea bacteria in men who have sex with men (MSM), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The CDC estimates that around 1 in 10 sexually active adults has chlamydia and an estimated 1 in 3 people ages 14-24 are infected with gonorrhea.
It is possible for epididymitis to spread through oral sex, but it is very unlikely. There are a number of STDs that can be transmitted through the mouth, but they are generally not considered especially common.
There are two types of infection one can get through oral sex: viral and bacterial. The most common viral STD is herpes (which can also be spread by skin-to-skin contact), and this one is rarely transmitted from mouth to genitals. The most common bacterial STD is chlamydia, and this can also be transmitted from mouth to genitals (although it’s unlikely in your case).
Generally speaking, it’s very unlikely for any STD to spread from mouth to genitals because saliva does not contain any of the necessary ingredients for infection. This is why doctors advise against sharing straws or other objects like toothbrushes or utensils when sick with a sore throat — even though you might think that sharing objects like these would help prevent passing on germs!
Epididymitis is a painful inflammation of the epididymis, a tube that stores sperm. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs), injury or trauma to the scrotum, or infection of the prostate gland.
Epididymitis typically occurs in men between ages 20 and 40 and is most common during summer months and after strenuous exercise.
Epididymitis can sometimes be transmitted to a partner through oral sex, but it’s not a common way for STIs to spread.
For more information about how STIs are spread and how you can protect yourself and your partner, visit Planned Parenthood’s Sexual Health site at https://www.plannedparenthood.org/sexual-health/stds
The epididymis is a tube that connects the testicle to the vas deferens. It’s where sperm matures and passes into the vas deferens.
Infections of the epididymis are usually caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia, gonorrhea, or non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU).
The infection can spread from your genitals through your bloodstream to your epididymis. If you have an STI in your throat or mouth, it can spread through oral sex if you are not using protection.
If you do have an STI in your mouth, it’s important that you get tested for other STIs as well.
How long is epididymitis contagious?

How long is epididymitis contagious?
The answer to this question depends on whether you have a bacterial or non-bacterial form of the disease.
Bacterial epididymitis is usually caused by infection with different types of bacteria, such as Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It’s important to remember that these infections are not transmitted by sexual contact alone. Instead, they’re typically passed from person to person through vaginal, oral or anal sex when one partner has an infected sore on his or her genitals that gets rubbed up against another person’s sexual organs. In other words, you can’t get a bacterial infection from just having sex with someone who has it; you have to have sexual contact with their infected genitals, too.
Once an infection enters the body through these means, it travels down into the epididymis and causes inflammation there. The most common symptom of a bacterial infection is pain in one side of your scrotum that’s worse when you move around and better when you lie still. Other symptoms include: fever; chills; nausea; vomiting; diarrhea; aches in your lower back and legs (because of your swollen testicles); and enlarged lymph nodes in
How long is epididymitis contagious?
The most common cause of epididymitis is infection with the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. In some cases, epididymititis can also be caused by chlamydia or non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU).
Epididymitis can be contagious if you have an STD, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, which causes it. It’s also possible for someone to spread the infection to others before they even know they have it.
If you think you have an STD, it’s important to get tested and treated as soon as possible. This will help prevent you from passing the infection on to others — including people who may not know they’re infected themselves.
The infection that causes epididymitis is contagious. That means that you can give it to others. In most cases, you might also be at risk of getting it from others.
How long is epididymitis contagious?
Epididymitis is contagious for up to 4 weeks after symptoms start. But you should avoid having sex until your doctor says it’s safe. It usually takes about 7 days on antibiotics for a person with epididymitis to clear the infection from their body and be able to have sex without passing it on to their partner.
Epididymitis is a painful inflammation of the epididymis, a tubular structure located on top of the testicle. It can be caused by a bacterial infection or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Epididymitis is common among sexually active young men who are exposed to chlamydia or gonorrhea. It can also occur after an STD that causes urethritis, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
The condition is contagious during the acute phase, which lasts from two days to two weeks after symptoms appear. It may also be spread through sexual contact during this time.
