The subcarinal lymph node (or pre-tracheal lymph node) is a lymph node located in the superior mediastinum of the thorax, posterior to the arch of aorta and the roots of both lungs. It is present at birth, but does not become conspicuous until after puberty.
The subcarinal lymph node receives drainage from the bronchial tree, esophagus, heart, and diaphragm. The efferents from this node travel to either paratracheal or paraaortic groups.[1]
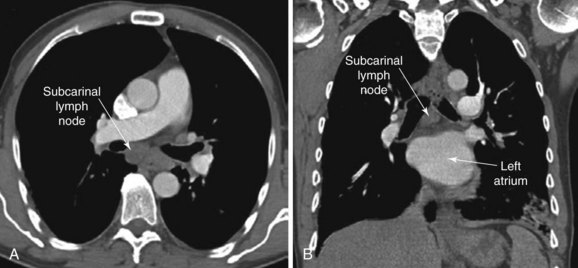
subcarinal lymph node
subcarinal lymph nodes are always present and are usually located just to the left of the tracheal bifurcation; they receive drainage from the bronchus intermedius, inferior pulmonary ligament, pulmonary hilum and mediastinal pleura; they are considered part of the para-aortic group of lymph nodes.
The subcarinal lymph node is a lymph node located in the left side of the thorax. It is one of the few lymph nodes which is found within the lungs. It is commonly involved in metastatic spread to regional lymph nodes from lung cancer.
The subcarinal lymph node (a.k.a. the subaortic node) is the largest lymph node in the mediastinum, which is the area in the chest between the lungs. As with all lymph nodes, it functions to filter fluid as it passes through the lymphatic system. This lymph node receives drainage from areas of the lung (via bronchomediastinal and intercostal trunks) and esophagus (via esophageal nodes). It also drains directly into the thoracic duct.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are at the bifurcation of the trachea, in the angle between the bronchi. These nodes receive venous blood from the lower border of the arch of aorta.
They receive lymph from:
the lungs
the bronchi and trachea
The subcarinal lymph nodes are located at the bottom of the trachea, and may contain metastatic breast cancer.
This is a lymph node that has been blocked for a long time. It may have been blocked by an infection or cancer. The blockage can cause the lymph node to swell and get bigger.
This node is near the main airways. This can make it hard to breathe. A surgeon may remove it. You will be given general anesthesia (you will be asleep). The surgery is done through a small cut in your chest wall. This is called thoracotomy
The subcarinal lymph node is a large lymph node that is located in the region where the trachea and right main bronchus divide. It lies in the concavity of the right side of the aortic arch, close to its bifurcation.
It receives lymph from the lower lobes of both lungs, and has efferent vessels that drain into the mediastinal (paratracheal) nodes, middle deep cervical nodes and bronchomediastinal trunk on left, and middle deep cervical nodes on right.
The subcarinal lymph node is important as it is one of several sites where cancerous cells may spread to via lymphatic channels.
Subcarinal lymph node: The subcarinal lymph node is a large lymph node that is located where the trachea (windpipe) divides into the left and right main bronchi.
The subcarinal lymph node is an important station for the drainage of fluid from the left lung (and to a lesser extent the right lung). Fluid that drains through a network of lymph channels from the lungs will end up at this lymph node. Subcarinal means below or beneath the root of the heart.
The subcarinal lymph node is a large lymph node found in the root of the neck. It is located at the lower end of the windpipe (trachea) immediately below the junction with the right main bronchus.
It is one of several key lymph nodes where cancer cells can spread to from the lungs and is therefore important to assess in lung cancer staging.
The subcarinal nodes are the lowermost mediastinal lymph nodes, and lie at the bifurcation of the trachea, overlying the left main bronchus.
It is a lymph node located at the subcarinal position. It is a fairly large lymph node that receives lymphatic drainage from the bronchial tree and the heart. Its efferent lymphatic duct drains into para-aortic lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes are round or oval-shaped and range in size from a few millimeters to about 1 centimeter (less than half an inch) in diameter. They have a fibrous capsule, a cortex and a medulla.
The cortex is the outer portion of the lymph node, and is usually divided into an outer cortical nodule (or nodules) and an inner cortical area. The cortex contains B cells, T cells, dendritic cells and macrophages. The medulla is the inner portion of the lymph node and often contains Hassall’s corpuscles (specialized collections of lymphocytes).
Lymph nodes associate with lymphatic vessels to drain lymph. The afferent vessels bring lymph into the node. The efferent vessels take it away. Lymph nodes are found along these vessels, at junctions between segments of lymphatic vessel (called collecting vessels), or in the vicinity of organs that generate large amounts of lymphocytes, such as bone marrow and spleen.
There are several groups of nodes in the head and neck: posterior cervical, anterior cervical, submandibular, submental, occipital, auricular (mastoid), buccal, superficial parotid, deep parotid and retropharynge
These are the lymph nodes at the base of the heart and adjacent to the trachea. They lie in a depression known as the cardiac impression or the subcarinal recess. If enlarged, they may be palpated through the chest wall. They are part of station 7 lymph node group and drain the trachea, main stem bronchi, esophagus, cardiac muscles, and diaphragm.
The lymph nodes near the junction of the trachea and the mainstem bronchi (subcarinal lymph nodes) receive lymphatic drainage from the esophagus, the lungs, and mediastinum. Any tumor in these sites will drain to the subcarinal lymph nodes. These nodes are best evaluated by CT scan or by mediastinoscopy.
The subcarinal node is a large lymph node in the paratracheal area, just beneath the carina. It is considered the last lymph node that drains lung tissue, before it drains into the thoracic duct. It is one of several stations in the lymphatic drainage of the lung called “station 7.”
The subcarinal lymph node may be visualized on a chest x-ray as a round opacity at this location; it is sometimes called “the egg between two slices of bread” for its appearance on an anteroposterior radiograph.
When this lymph node is enlarged due to disease processes in the lungs (such as lung cancer or tuberculosis), it may be biopsied using a mediastinoscopy procedure.
The subcarinal lymph node is a large lymph node that sits at the bifurcation of the trachea and bronchi.
It is not normally palpable because of its location, but may be enlarged in diseases such as tuberculosis and lymphoma.
- The subcarinal lymph node is the largest lymph node in the lower respiratory tract. It is located at the confluence of the left and right bronchopulmonary segmental veins, where they empty into the pulmonary veins. Because of this location, the subcarinal lymph node receives drainage from most of the left lung as well as about half of the right lung.\n- The left inferior pulmonary ligament is a thin fold of pleura that extends inferiorly from the hilum to the apex of the lung, where it is continuous with the visceral pleura. This ligament contains a collection of lymph nodes (pulmonary ligament lymph nodes) that receive drainage from segments 5 and 8 of the lower lobe.
where is subcarinal lymph node

The subcarinal lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes located at the base of the pulmonary artery, in between the bifurcation of the trachea and left main bronchus and the superior vena cava. The esophagus passes posteriorly to these lymph nodes.
The subcarinal lymph node is also known as Carinal Lymph Node.
The subcarinal lymph node is the largest lymph node station in the tracheobronchial tree and also one of the most common sites of metastasis. It is located at the bifurcation of the main bronchi.
The subcarinal space is a small pouch located at the junction of the trachea and the right main bronchus. It is also called the right paratracheal space, right paratracheal recess, or subcarinal recess. The lymph nodes that lie in this space are called the Subcarinal lymph nodes.
The Subcarinal lymph nodes are located in between the lower part of the trachea and esophagus and the upper part of the right main bronchus. They are well defined structures with an oval shape.
Their position is posterior to the trachea and anterior to the esophagus and heart.
Subcarinal lymph nodes are covered by a fibrous capsule, which separates them from other nearby structures like vertebrae, thoracic duct, oesophagus, pulmonary artery and vein, aorta and its branches namely left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery, superior vena cava and superior intercostal artery.
The subcarinal lymph node is at the junction of the right main bronchus and trachea.
Subcarinal lymph nodes (sometimes referred to as the station 7 lymph nodes) are located below the heart and in front of the vertebral column. These lymph nodes drain tissues from the trachea and bronchi, esophagus, thymus, pericardium, mediastinum and lungs.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are located posterior to the heart, at the junction of the trachea and bronchus. The subcarinal lymph nodes may be involved in cancer spread from the lung and may be visualized on PET/CT imaging.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are situated at the bifurcation of the trachea, behind the junction of the left main bronchus and the right pulmonary artery.
These lymph nodes drain lymph from the left lung apex, hilum, and mediastinum.
The lymph node stations in the mediastinum are divided into anterior and posterior. The anterior stations include the pretracheal, paratracheal, and pre-esophageal nodes. The paratracheal nodes are subdivided into upper, middle, and lower groups. The posterior stations include the subaortic, tracheobronchial, pulmonary ligament, hilar, interlobar, and basal stations
The subcarinal lymph node is located just below where the trachea and left primary bronchus bifurcate. It is part of the tracheobronchial lymph node station.
Numerous studies have shown that staging accuracy for lung cancer can be greatly improved by nodal sampling beyond the hilar nodes to include mediastinal (tracheobronchial) lymph nodes.
This paper reviews the anatomy of this lymph node station with a particular emphasis on its position relative to malignant tumors arising in the hilum or lower lobe of the lung
Subcarinal lymph nodes are a group of lymph nodes located just behind the heart, in the subcarinal space. They are the largest group of mediastinal lymph nodes.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are located at the bottom left side of the heart, near the aorta. The aorta is the body’s main artery, which branches into smaller arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are responsible for removing toxins and waste from the lymphatic system, as well as filtering out harmful substances in the blood that pass through on their way to other parts of the body.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are located at the bifurcation of the trachea.
Lymph node involvement in patients with lung cancer is often found in the hilar, interlobar, subcarinal and ipsilateral mediastinal nodes.
The subcarinal lymph nodes are located at the bottom of the trachea below the junction of the bronchus, or airway, that leads to the right lung.
The subcarinal nodes are found in front of the aortic hiatus, behind the bifurcation of the trachea. They receive lymphatic vessels from most bronchial lymph nodes and may also drain some lung tissue. The right subcarinal node is often enlarged, particularly when a superior vena caval obstruction is present.
The right subcarinal node along with all other nodes along the tracheobronchial tree of the lung on the right side are referred to as the pulmonary ligament (ligamentum pulmonale).